2020. 7. 29. 09:00ㆍSky observation
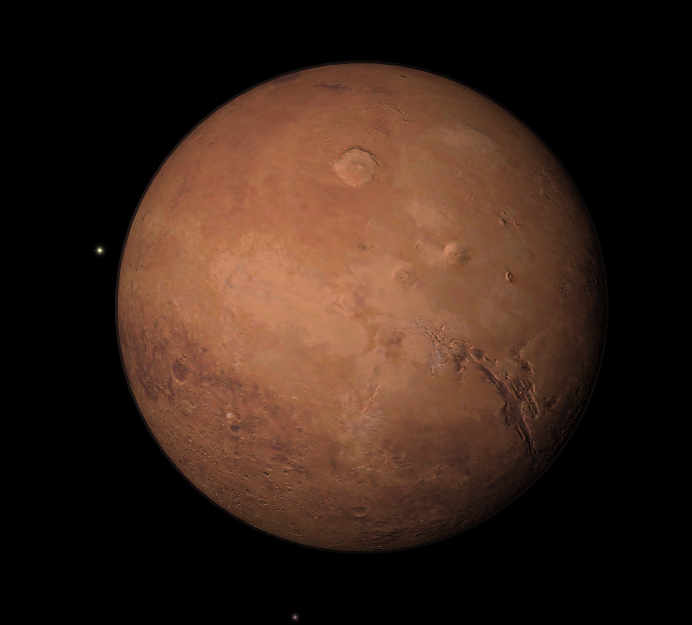
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, and has been known since ancient times for its reddish color. Mars is named after the Roman god of war, and takes that name from its color. Perhaps because its bloody hue, its close proximity to Earth, and its seasonally-changing surface features, Mars has played a larger role in human culture and mythology than any other planet.

Orbit and Observation
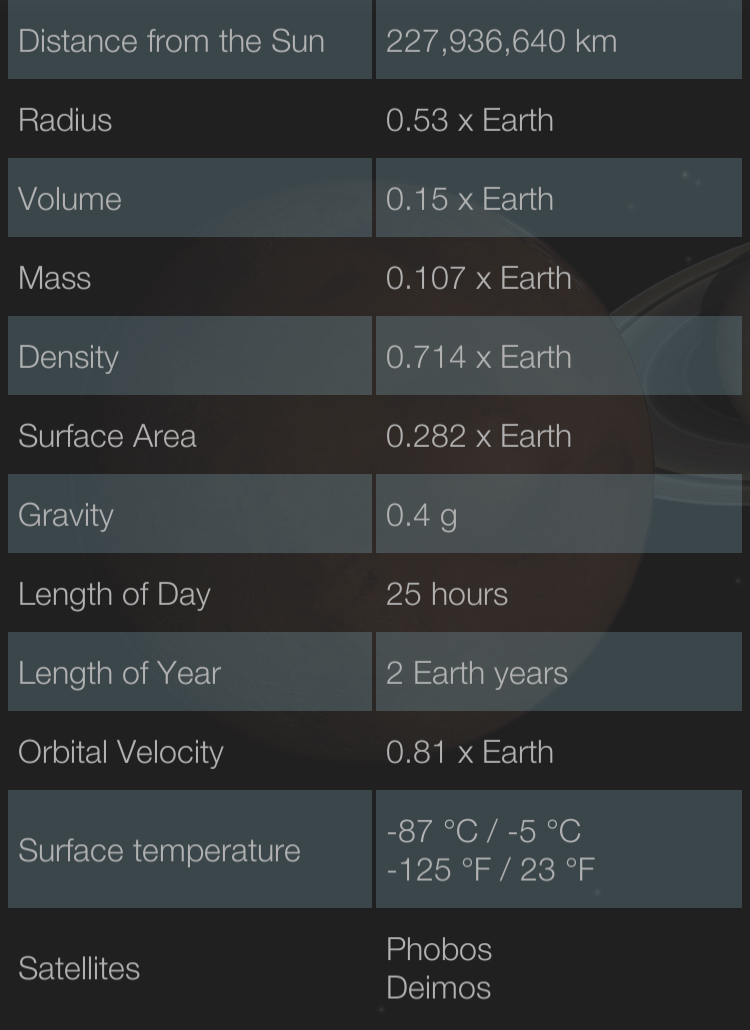
Mars orbits the Sun at about 1.5 times the average distance of the Earth, with a an orbital period of 687 days. Mars's orbit eccentricity (0.0934) is about six times greater than the Earth's, so its distance from Earth varies widely 59 million km at a "favorable" opposition near the orbit's perihelion, to 399 million km at superior conjunction near its aphelion. Because of this, Mars varies greatly in its apparent size, from 3.5 to 25 arc seconds, and in brightness from magnitude -2.9 to +1.7.
In a small telescope, Mars shows many of the surface features that sparked the imagination of science fiction writers.
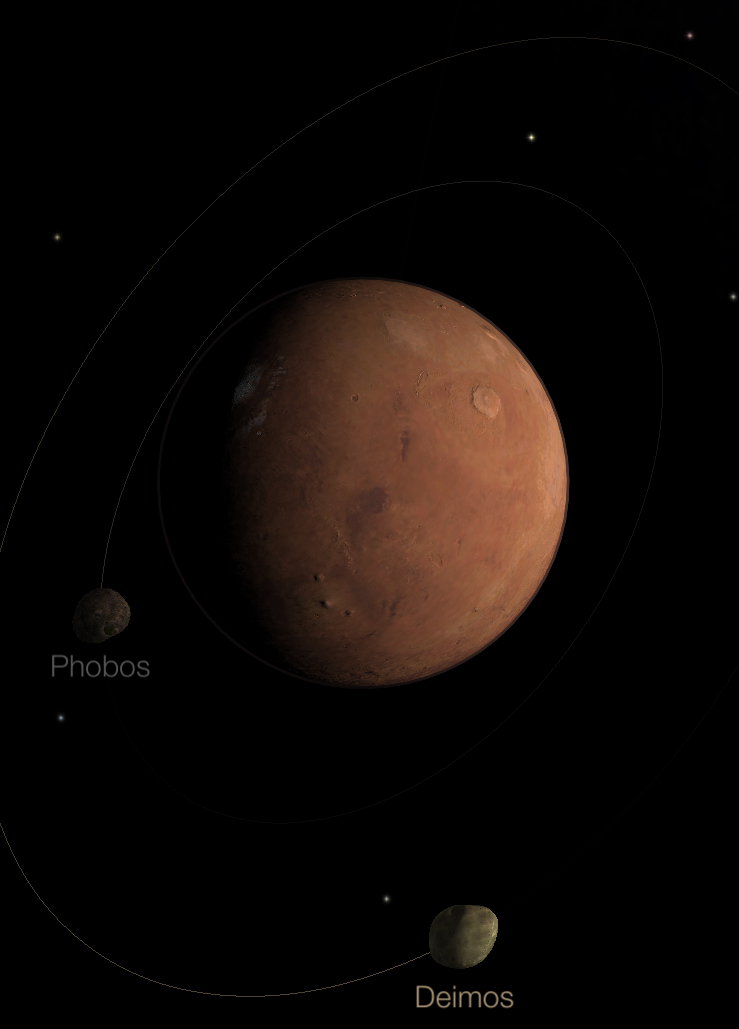
Prominent white polar caps are visible, as are odd dusky markings on its surface. These markings show that Mars rotates once every 24 hours and 37 minutes - so its day is almost the same length as Earth's. Mars also has an axial tilt very similar to Earth's, and has seasons like the Earth. The polar caps shrink and expand during the Martian summer and winter, and the dark patterns on its surface also display seasonal changes. Mars has an atmosphere with sparse clouds, and exhibits occasional dust storms which sometimes grow to cover the entire planet's surface for a few weeks.
The tallest volcano and The deepest and longest canyon solar system
The tallest of the volcanoes, Olympus Mons ("Mount Olympus"), is about 17 miles (27 km) high - about three times the elevation of Mount Everest! - and is 340 miles (550 km) across at its base. Olympus Mons is both the largest volcano and the tallest mountain in the solar system, and is aptly named for the home of the gods.
The deepest and longest canyon system on Mars is Valles Marineris (the "Mariner Valley"), and is up to 7 km)deep, 200 km wide, and 5000 km long. It is the largest known crevice in the solar system
Air and Water on Mars
More importantly, spacecraft images showed surface features that seemed to indicate the presence of water: channels, dry riverbeds, and flood plains. Features such as these look strikingly similar to features on Earth which have been created by liquid water. But on Mars, unlike Earth, liquid water is all but nonexistent today.
Currently, most of Mars's water is buried beneath the surface or frozen as ice in the polar caps. Mars's permanent polar caps are made of water ice; the seasonal expansion and contraction of the polar caps is actually due to the presence of carbon dioxide ice freezing out of the atmosphere - Mars's polar regions never become warm enough for water to melt.
Summary
'Sky observation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 토성- Saturn- (0) | 2020.08.04 |
|---|---|
| 행성 목성 -Planet Jupiter (0) | 2020.07.30 |
| 행성 금성 Planet Venus (0) | 2020.07.28 |
| MEADE ETX125 OBSERVER (0) | 2020.07.26 |
| 천문학 -Astronomy (0) | 2020.07.22 |