2020. 7. 30. 09:40ㆍSky observation
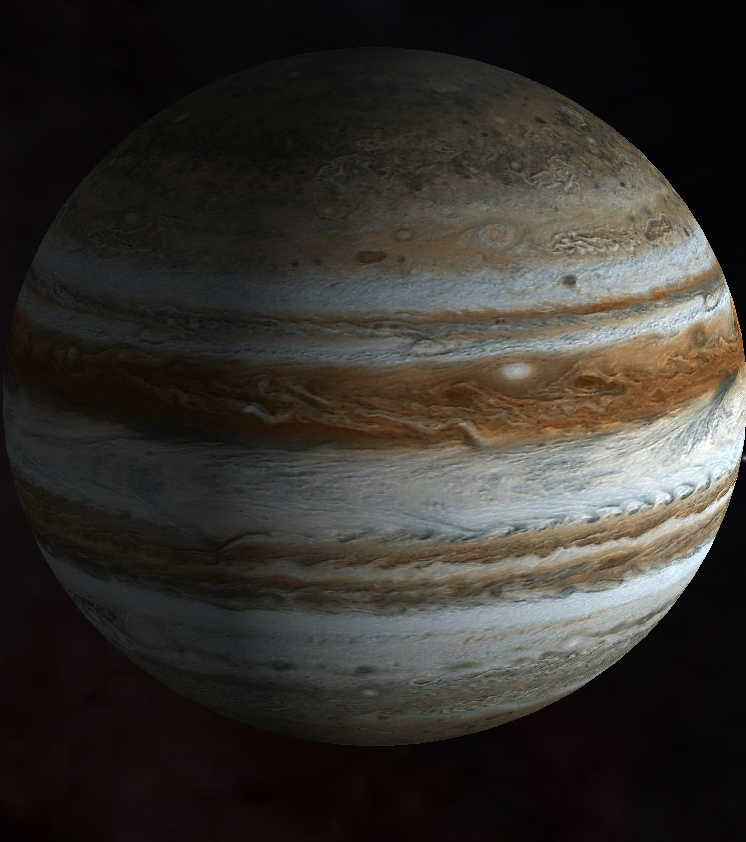

Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system, and by far the most massive. It contains over twice as much matter as all of the other planets combined. Jupiter is a very different planet from the Earth, or any of the other inner planets. It is composed mostly of liquid and gaseous hydrogen, and has no solid surface. For this reason, Jupiter is the first of the "gas giant" planets.
Observation and Exploration
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun, and orbits at an average distance of 480 million miles (780 million km) from it - that is, 5.20 times as far as the Earth. Jupiter takes 11.86 years to complete one orbit around the Sun. With an equatorial diameter of about 89,000 miles (143,000 km), Jupiter is over 11 times the diameter of the Earth. In spite of its size, Jupiter is the fastest-rotating planet, taking only 9 hours and 56 minutes to complete one rotation. Because of its rapid rotation, Jupiter is noticeably flattened at the poles.
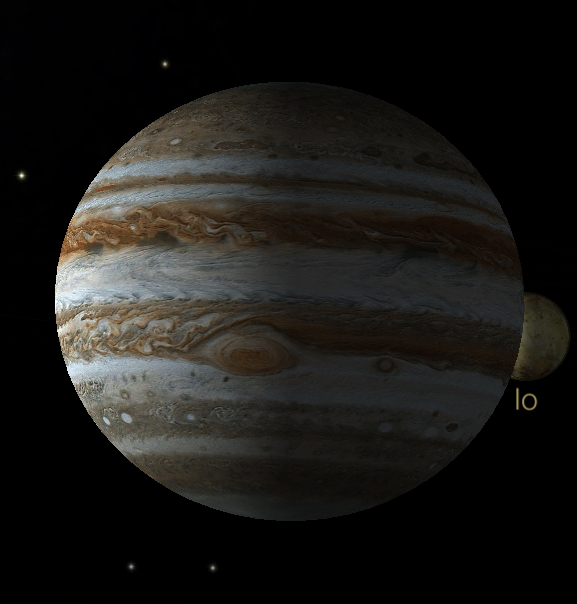
Jupiter is large enough, and close enough to Earth, to show features that are easily visible in a small telescope. The most prominent are the equatorial bands, which look like brownish stripes. Higher magnification will reveal many more features, and show the complexity of Jupiter's atmosphere. The most prominent feature visible to small telescopes is the Great Red Spot (GRS). This is a long-lived cyclone in Jupiter's southern hemisphere; it has lasted for at least 300 years, and is larger than the entire Earth. It rotates counter-clockwise in about six days and, interestingly, moves in the opposite direction as the cloud belts around it.
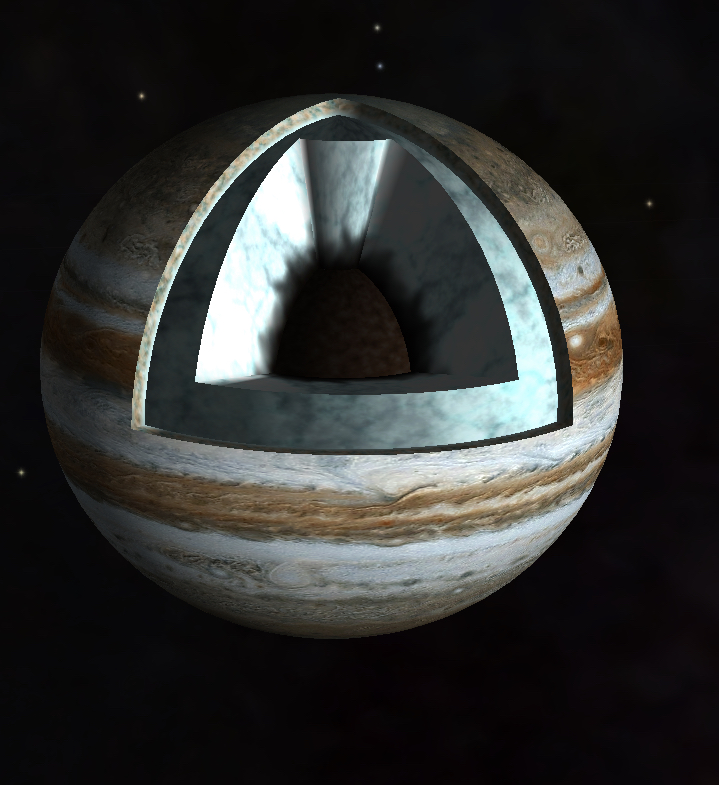
Internal Structure
Beneath the clouds, the atmospheric pressure rises quickly, compressing the hydrogen and helium into a liquid state. Further down, the pressure is so great that electrons are stripped from hydrogen atoms, and wander freely through the planet's interior like those in a metal. This liquid metallic hydrogen comprises the bulk of Jupiter's mass. At its center, Jupiter may possess a core of rocky material about the size of the Earth.

Moons
Jupiter has four large moons, first discovered by Galileo in 1610: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. These "Galilean" moons are easily seen in a small telescope or even binoculars, lined up along Jupiter's equatorial plane. They move quickly in their orbits around Jupiter; one can see their motion relative to the planet over a period of a few hours. The shadows of the Galilean moons are often easily seen as well, transiting across the face of Jupiter. All four Galilean moons are tidally locked with Jupiter, forever showing the same face toward the giant planet.
The rest of Jupiter's 67 moons are small, less than 200 km in diameter. They are also dark, with albedos of about 0.04. They form a complex system, and are classified by their orbital properties into "families", in the same manner as asteroids. Most have retrograde orbits, and are in fact believed to be captured asteroids.
'Sky observation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 광학 망원경 유형 -Optical Telescope Types (0) | 2020.08.05 |
|---|---|
| 토성- Saturn- (0) | 2020.08.04 |
| 화성의 행성 Planet of Mars (0) | 2020.07.29 |
| 행성 금성 Planet Venus (0) | 2020.07.28 |
| MEADE ETX125 OBSERVER (0) | 2020.07.26 |